When you need to use a library in your C++ application you should tell the following things to the compiler:
- The name of the lib file
- The folder where to find the lib file
- The folder where to find the header file
In this post, I show how you can do this using Microsoft Visual Studio 2010. All the options are available as Properties of your current project.
Right click the project name under the Solution Explorer and select Properties from the dropdown menu:
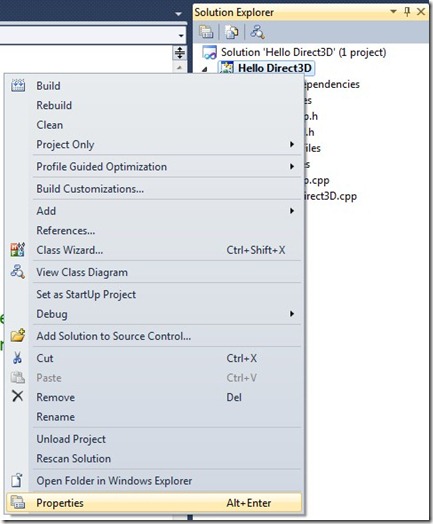
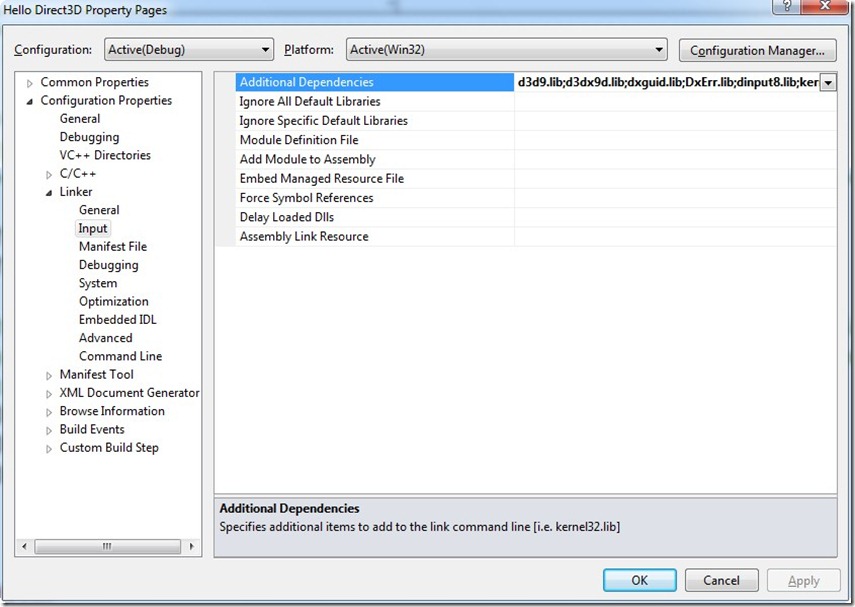
You can add all the names of your libraries in the “Configuration Properties –> Linker –> Input“ section:
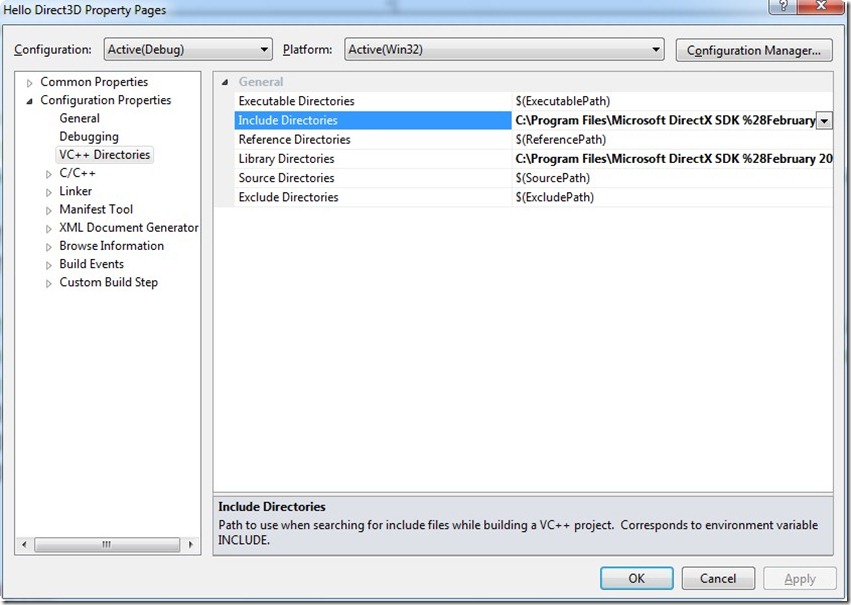
At the end, you can set the lib folders (“Library Directories”) and the headers folders (“Include Directories”) in the “Configuration Properties –> VC++ Directories” section.
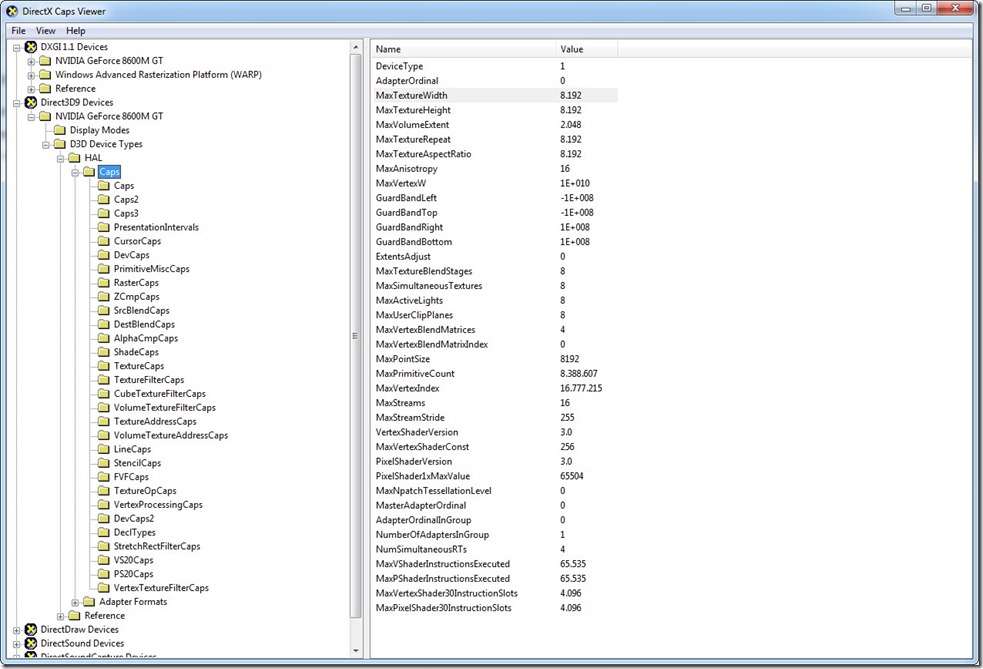
If you want to know the capabilities available in your graphics card you can use a tool in the DirectX SDK\Utilities\Bin\x86.
This tool is called “DXCapsViewer.exe”.
Here a screenshot with the capabilities of my NVIDIA GeForce 8600M GT:
You can download the latest DirectX SDK at the following link:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/directx/aa937788.aspx
Multisampling is an antialiasing technique directly supported by DirectX and obviously by XNA. The problem of aliasing occurs when you draw a line on a monitor with low resolution. In that cases you see a stair step when approximating a line by a matrix of pixels. Multisampling use neighbouring pixels (called samples) to calculate the final color of a pixel.
You can enable multisampling in XNA in this simple way:
graphics.PreferMultiSampling = true;
Then you should also specify two options.
The type is an enumerator (MultiSampleType) that represent the number of samples to use in multisampling. The quality is an integer that represent the quality level. This value is always set to zero. Before to set the type of multisampling you should always check if the graphic adapter support it using the method adapter.CheckDeviceMultiSampleType()
graphics.PreparingDeviceSettings += new EventHandler<PreparingDeviceSettingsEventArgs>((sender, e) =>
{
PresentationParameters parameters = e.GraphicsDeviceInformation.PresentationParameters;
parameters.MultiSampleQuality = 0;
#if XBOX
pp.MultiSampleType = MultiSampleType.FourSamples;
return;
#else
int quality;
GraphicsAdapter adapter = e.GraphicsDeviceInformation.Adapter;
SurfaceFormat format = adapter.CurrentDisplayMode.Format;
if (adapter.CheckDeviceMultiSampleType(DeviceType.Hardware, format, false, MultiSampleType.FourSamples, out quality))
{
parameters.MultiSampleType = MultiSampleType.FourSamples;
}
else if (adapter.CheckDeviceMultiSampleType(DeviceType.Hardware, format, false, MultiSampleType.TwoSamples, out quality))
{
parameters.MultiSampleType = MultiSampleType.TwoSamples;
}
});
For more information:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multisample_anti-aliasing
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb975403.aspx
I would like to inform you that an interesting stable project is available on codeplex. This is the Nuclex Framework.
This is the main page of the project:
http://nuclexframework.codeplex.com/
The more interesting features for me are the following: